Overview of Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a widely used diagnostic imaging exam that uses sound waves to create real-time images of organs, soft tissues, and blood flow inside the body. Unlike x-rays and CT scans, ultrasound does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safe and noninvasive option for patients of all ages, including pregnant women and an unborn baby.
For reliable, radiation-free ultrasound imaging using advanced technology, visit Sound Waves Imaging and explore our diagnostic imaging services.
Advanced Ultrasound Imaging for a Clear Diagnosis
Modern ultrasound imaging uses the latest ultrasound technology to deliver clearer images and better accuracy for clinical decision-making. Sound waves bounce off internal structures and return as reflected waves, which are processed into a detailed sonogram.
Key benefits include:
- Real-time visualization of organs and soft tissues
- Precise assessment of blood flow with Doppler techniques
- Safe imaging with no ionizing radiation
- Fast results that support timely diagnosis and treatment options
This advanced imaging is often combined with other imaging exams to guide care.
Types of Ultrasounds
There are several types of ultrasound, each designed for specific diagnostic needs:
- Abdominal ultrasound: Evaluates the liver, gallbladder, kidney, spleen, aortic structures, and ureter
- Doppler ultrasound: Measures blood flow through arteries and veins
- Bladder ultrasound: Assesses bladder volume and urinary retention
- Transrectal ultrasound: Evaluates the prostate and rectum (urology)
- Transvaginal ultrasound: Examines ovary, fallopian tubes, implantation, and other female reproductive organs
- Scrotal ultrasound: Evaluates the scrotum and testicular structures
- Thyroid ultrasound: Assesses thyroid nodules and soft tissues
Ultrasound may also be used as part of a biopsy to guide accurate needle placement.
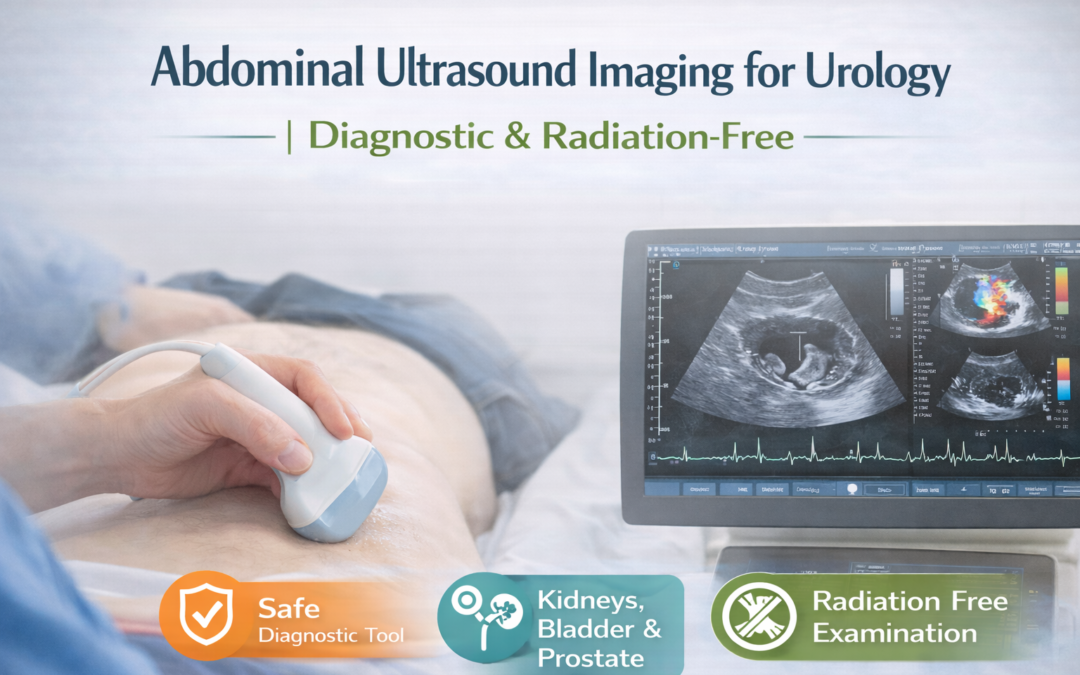
Abdominal Ultrasound
An abdominal ultrasound is a common ultrasound exam used to evaluate abdominal organs and the urinary tract. It is often performed for symptoms such as abdominal pain, swelling, abnormal blood tests, or suspected gallbladder or kidney problems.
This exam helps identify gallstones, cysts, organ enlargement, and blockages
What Are the Risks of Abdominal Ultrasound?
Abdominal ultrasound is extremely safe. Ultrasounds are noninvasive, do not require sedation, and do not expose patients to radiation. According to the American College of Radiology, diagnostic ultrasounds have no known harmful effects when performed by trained professionals.
Ultrasound Identification (USID)
Ultrasound Identification (USID) refers to the use of ultrasound technology to identify structures, objects, or boundaries based on returning sound waves. This principle is applied in medical diagnostics as well as industrial and scientific fields.
Ultrasonic Range Finding
Ultrasonic range finding uses sound waves to measure distance by calculating the time it takes for waves to bounce back from an object. This technology is widely used in navigation systems, robotics, and medical imaging equipment.
Ultrasonic Cleaning
Ultrasonic cleaning uses high-frequency sound waves in a liquid solution to remove contaminants from delicate instruments. In healthcare, it is commonly used to clean surgical and diagnostic tools safely and efficiently.
Ultrasonic Humidifier
An ultrasonic humidifier uses ultrasonic vibrations to produce a fine mist, helping maintain indoor air moisture. While not a medical imaging tool, it relies on similar ultrasound principles.
Test Details
An ultrasound exam is typically performed by a trained technologist using an ultrasound transducer or ultrasound probe. A water-based gel is applied to the skin; the gel helps transmit sound waves and improve image quality.
A radiologist reviews the images and shares results with your care team.
How Do I Prepare for an Ultrasound?
Preparation depends on the type of ultrasound:
- You may be asked to fast for abdominal exams
- A full bladder may be required for pelvic or bladder ultrasound
- Wear comfortable clothing
- Ultrasound exams don’t require special recovery time
Follow instructions provided by your imaging facility.
What Happens During an Ultrasound?
During the exam, gel is applied to your skin, and the ultrasound transducer is gently moved over the area being examined. Sound waves bounce off organs and tissues, creating detailed images on a monitor. Most exams take 20–45 minutes.
Are Ultrasounds Safe?
Yes. Ultrasound uses sound, not radiation. It is considered one of the safest medical imaging techniques and is commonly used to monitor pregnancy and evaluate soft tissues.
FAQs
1. What does an ultrasound check for?
Ultrasound is used to evaluate organs, soft tissues, blood vessels, cysts, tumors, and blood flow, and to monitor pregnancy.
2. What are three reasons why an ultrasound is done?
Ultrasound is done to diagnose medical conditions, guide procedures such as biopsy, and monitor treatment or pregnancy.
3. How do you prepare for an ultrasound?
Preparation may include fasting or drinking water for a full bladder, depending on the exam type.
4. Does an ultrasound have risks?
Diagnostic ultrasounds have no known risks and do not involve ionizing radiation.
5. Who might need an ultrasound?
Patients with abdominal pain, urinary issues, pregnancy, or suspected organ or vascular conditions may need an ultrasound exam.